Nafion-Initiated ATRP of 1-Vinylimidazole for Preparation of Proton Exchange Membranes
Abstract
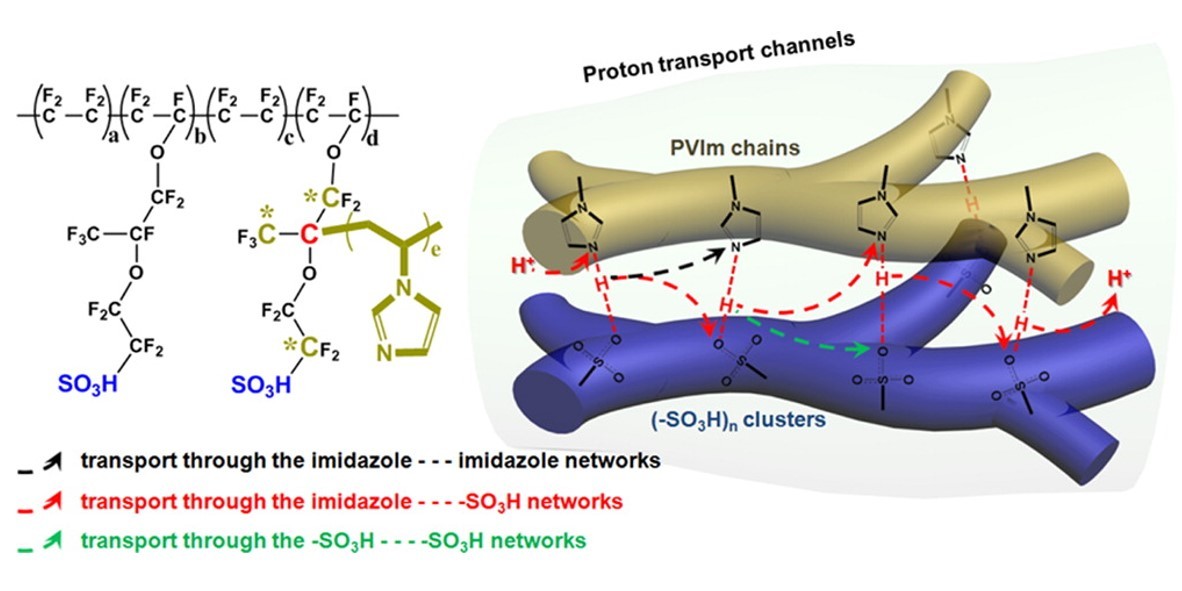
Nafion is one of the most widely investigated materials applied in proton exchange membranes. Interestingly, it was found that Nafion could serve as a macroinitiator to induce atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) on its C–F sites. In this study, poly(1-vinylimidazole) was selectively bonded on the side chains of Nafion via the Nafion-initiated ATRP process, which was confirmed by the measurements of 1H/19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectra, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimeter and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The as-prepared Nafion-co-poly(1-vinylimidazole) (Nafion-PVIm) membranes, with tunable loading amount of imidazole rings, presented greatly enhanced proton conductivity and methanol resistivity due to their well-controlled chemical structures. Especially, chemically bonding PVIm with Nafion chains endowed the Nafion-PVIm membranes with high stability in proton conductivity. For the first time, we revealed the great potentials of the Nafion-initiated ATRP process in developing high-performance proton exchange membranes.
<<全文链接>>

