In Situ Study of Diffusion and Interaction of Water and Electrolyte Solution in Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Membrane...
Citation
Beibei Tang, and Peiyi Wu*. In Situ Study of Diffusion and Interaction of Water and Electrolyte Solution in Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Membrane Using FTIR and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis. Vib. Spectrosc 2009, 51, 65-71.
Abstract
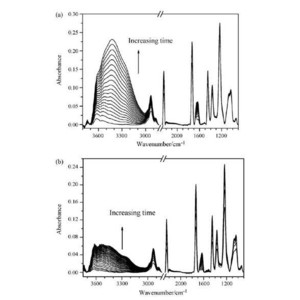
In the study, the diffusion process of water and CaCl2 aqueous solution in polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membrane have been investigated using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy and two-dimensional (2D) correlation analysis. In 2D ATR-FTIR spectra, the water ν(OH) band in PAN membrane during both water and CaCl2 solution diffusion is split into three separate bands. However, the OH band appearing from bound water which forms hydrogen-bonding of CaCl2 solution diffusion has a considerably lower wavenumber than that of pure water diffusion, which is due to association between Ca2+ions and the C