Insights Into the Thermal Phase Transition Behavior of A Gemini Dicationic Polyelectrolyte in Aqueous Solution
Citation
Yingna Zhang, Hui Tang, and Peiyi Wu. Insights into the Thermal Phase Transition Behavior of a Gemini Dicationic Polyelectrolyte in Aqueous Solution. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 4380-4387.
Abstract
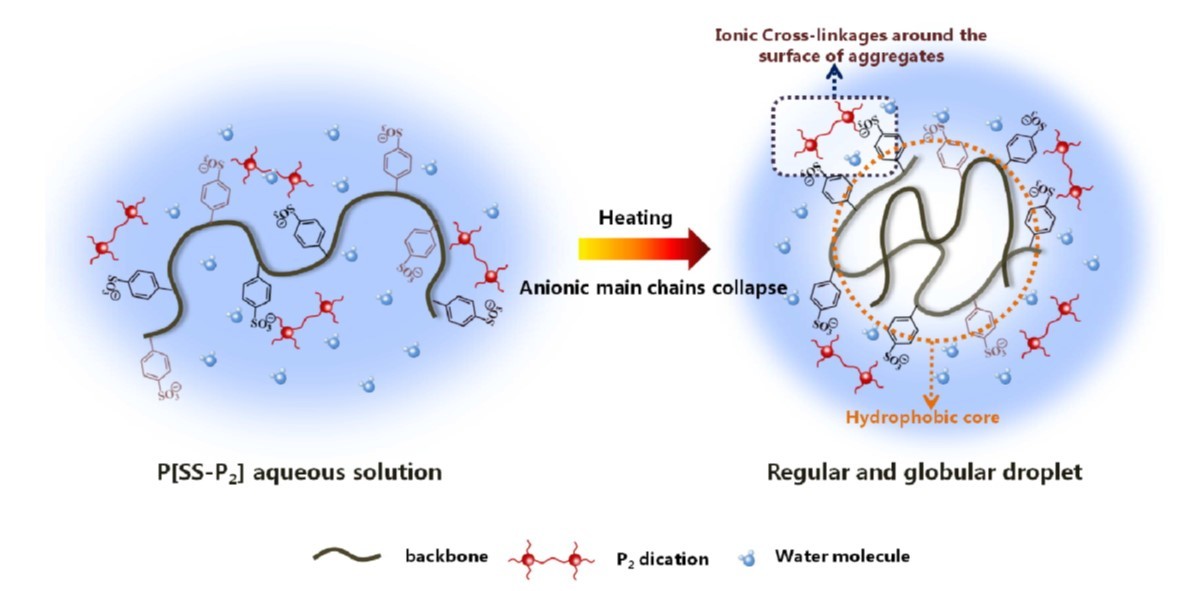
Thermal-induced phase transition behavior of a LCST-type poly (ionic liquid) (PIL) aqueous solution with gemini-cationic structure, poly [(1, 8-octanediyl-bis(tri-n-butylphosphonium) 4-styrene sulfonate] (P[SS-P2]), was investigated in this paper. Based on the calorimetric measurements, unique dependence of transition points on concentrations was found in P[SS-P2] aqueous solution compared to its mono-cationic PIL and [SS-P2] aqueous solution. Optical microscopy showed that globular microscopic droplets were formed during the phase transition, suggesting that gemini dications and the possible dynamic ionic bonds may facilitate the liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) in P[SS-P2] aqueous solution. Temperature-variable 1H NMR and FT-IR investigations manifested that the dehydration of anionic chains instead of the dehydration of dications served as the driving force of the phase separation in the P[SS-P2] aqueous solution, implying that the polymerized anions tended to aggregate together firstly and lied in the core with dications distributed around the globules at the end of transition process. Notably, considering that the SO3 groups in the gemini-cationic system tended to be distributed around the surface of collapsed anionic main chains rather than be wrapped into the aggregates, it is supposed that the dynamic ionic bonding between dication and anionic backbones were distributed in the periphery of globules and acted as the “cross-linkers” which enhanced the stability of regular droplets after the phase transition in P[SS-P2] aqueous solution.