Effect of Small Amount of Ultra High Molecular Weight Component on the Crystallization Behaviors of Bimodal...
Citation
Shijie Song, Peiyi Wu, Minxing Ye, Jiachun Feng*, and Yuliang Yang. Effect of Small Amount of Ultra High Molecular Weight Component on the Crystallization Behaviors of Bimodal High Density Polyethylene. Polymer 2008, 49, 2964-2973.
Abstract
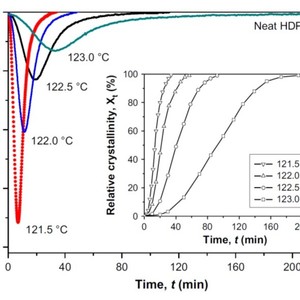
In order to clarify the effect of high molecular weight component on the crystallization of bimodal high density polyethylene (HDPE), a commercial PE-100 pipe resin was blended with small loading of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). The isothermal crystallization kinetics and crystal morphology of HDPE/UHMWPE composites were studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and polarized optical microscopy (POM), respectively. The presence of UHMWPE results in elevated initial crystallization temperature of HDPE and an accelerating effect on isothermal crystallization. Analysis of growth rate using Lauritzen–Hoffman model shows that the fold surface free energy (σe) of polymer chains in HDPE/UHMWPE composites was lower than that in neat HDPE. Morphological development during isothermal crystallization shows that UHMWPE can obviously promote the nucleation rate of HDPE. It should be reasonable to conclude that UHMWPE appeared as an effective nucleating agent in HDPE matrix. Rheological measurements were also performed and it is shown that HDPE/UHMWPE composites are easy to process and own higher melt viscosity at low shear rate. Combining with their faster solidification, gravity-induced sag in practical pipe production is expected to be effectively avoided.