Effect of β‐nucleating agents on crystallization and melting behavior of isotactic polypropylene
Citation
Wenchang Xiao, Peiyi Wu, and Jiachun Feng*. Effect of β-Nucleating Agents on Crystallization and Melting Behavior of Isotactic Polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 3370-3379.
Abstract
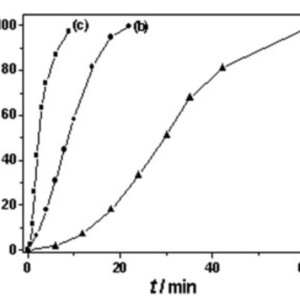
Two kinds of β-nucleating agents, named a rare earth complex (WBG) and a N,N′-dicyclohexylterephthalamide (TMB5), were introduced into isotactic polypropylene (iPP), and their effect on crystallization and melting behavior of iPP was comparatively investigated. Wide angle X-ray diffraction measurements revealed that both the two additives were highly effective in inducing β modification. At their respective optimum concentrations of 0.08 wt % for WBG and 0.06 wt % for TMB5, the relative amount of β-form calculated by Turner-Jones equation both exceeds 92%. However, the isothermal crystallization kinetics investigated by differential scanning calorimetry demonstrated that WBG had more pronounced effect than TMB5 in accelerating the overall crystallization rate. The Lauritzen–Hoffman theory analysis also revealed that WBG was more effective not only in increasing the nucleus number but also in accelerating the growth rate of crystallization. After completing isothermal crystallization process, the subsequent melting behavior examination suggested that the addition of WBG expanded the upper limit temperature of forming β modification, and therefore was more effective in delaying the β-α transformation than TMB5.