MWNTs/Polyester Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane: An Approach to Overcome the Trade-Off Effect between Permeability...
Citation
Huiqing Wu, Beibei Tang*, and Peiyi Wu*. MWNTs/Polyester Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane: An Approach to Overcome the Trade-Off Effect between Permeability and Selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16395-16400.
Abstract
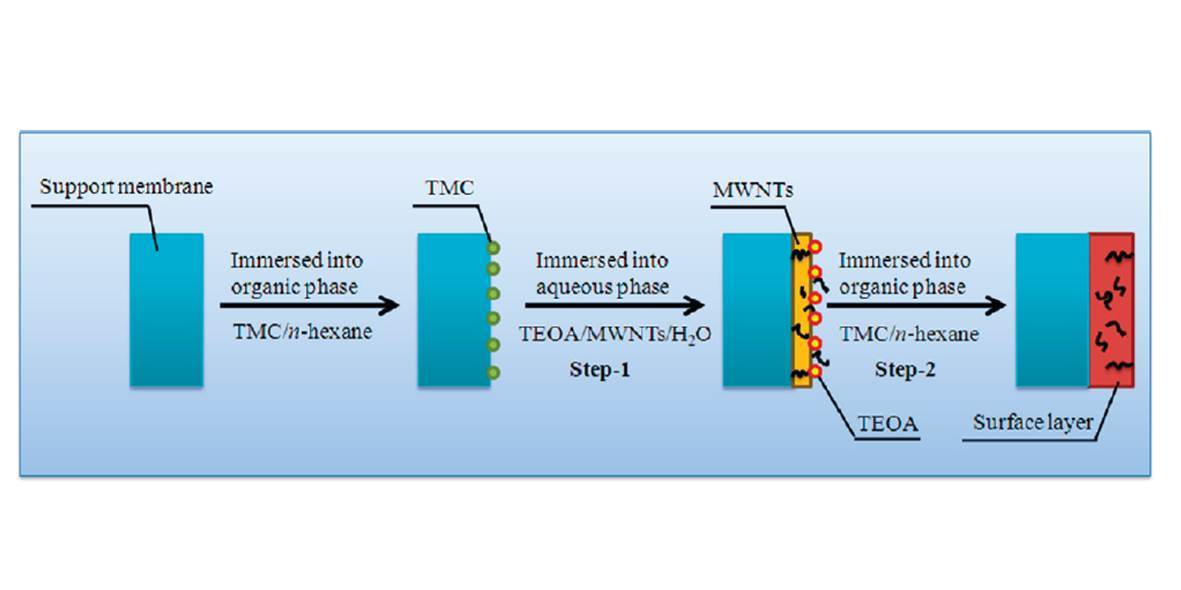
An improved process to prepare MWNTs/polyester thin film nanocomposite membranes was initiated by interfacial polymerization of trimesoyl chloride (TMC) and triethanolamine (TEOA) solution containing MWNTs. The improved process was facilely done by immersing the support membrane into the organic phase before the conventional process of interfacial polymerization. The TEM images showed that the MWNTs were embedded throughout the polyester thin film layer. The MWNTs/polyester thin film nanocomposite membrane prepared via the improved process exhibited both high permeability and excellent selectivity when compared with the thin film composite membrane without MWNTs and the MWNTs/polyester thin film nanocomposite membrane prepared via the conventional process. The water permeability increased upon an increase of reaction time of TMC-saturated support membrane immersed into aqueous phase (step-1), reaching a maximum of 4.7 L/m2 h at 25 min, while the membrane rejection rate kept increasing. The role of step-1 played a positive role in the performance and the morphology of the thin film composite membrane. It was found that the process of step-1 produced a low degree of cross-linking thin layer with high amount of hydrophilic and negatively charged carboxyl groups. This improved process of interfacial polymerization to prepare MWNTs/polymer thin film nanocomposite membranes provides a new approach to overcome the trade-off effect between permeability and selectivity.