Annealing of Melt-Crystallized Polyethylene and Its Influence on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties...
Abstract
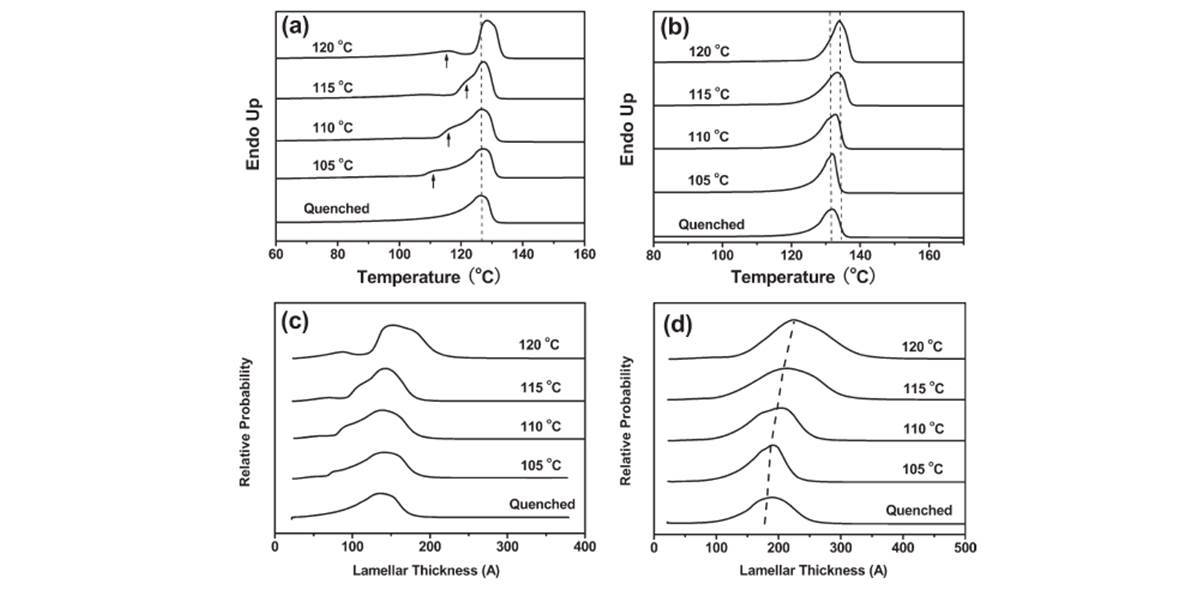
Annealing treatments have been performed on two melt-crystallized polyethylenes (PE) with different topologies, namely highly branched and linear PE, to comparatively investigate the microstructural evolution and corresponding changes of mechanical property. It shows that annealing induced different degrees of variation in the lamellar rearrangement of the two PEs. Branched PE, which incorporates comonomers on the backbones, shows a more versatile annealing effect when compared with the linear counterpart. With respect to PEs, it is for the first time a connection was made between the annealing-induced microstructural changes and an important but less understood property known as heat distortion temperature (HDT). It shows that at lower annealing temperatures, the improvement of HDT can be well correlated to the increased crystallinity induced by lamellar rearrangement for both PEs. However, for branched PE, the contribution of crystallinity is weakened at higher annealing temperatures and the dominant factor on HDT was replaced by the relaxation of lamellar structure. © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 49: 1347–1359, 2011.
<<全文链接>>

