Optimizing Polyamide Thin Film Composite Membrane Covalently Bonded with Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
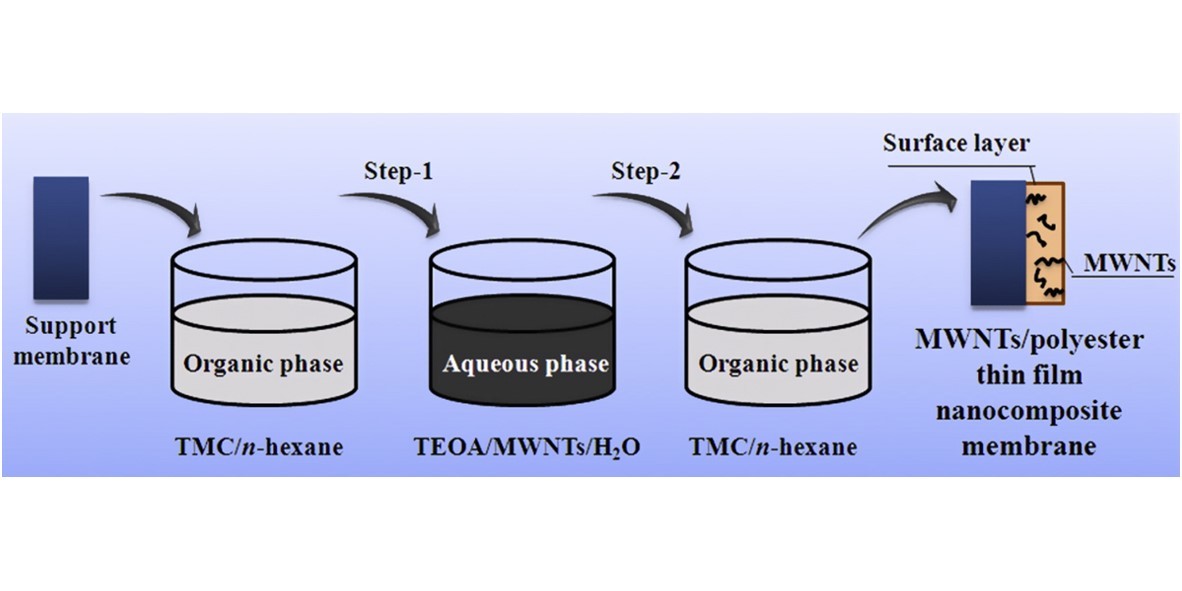
MWNTs/polyester thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes were prepared through an improved process by interfacial polymerization of triethanolamine (TEOA) and trimesoyl chloride (TMC) on the polysulfone (PSf) supporting membrane in the presence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs). The effect of MWNTs concentration and surfactant species in the aqueous phase as well as the reaction time of interfacial polymerization on the membrane properties were investigated. The water permeability increased as the MWNTs concentration in aqueous phase increased up to 0.5 mg/mL, reaching a maximum which was nearly double that of the thin film membrane without MWNTs, while the membrane rejection kept increasing dramatically. Compared with cationic (CTAB) and non-ionic (Triton X-100) surfactants, anionic (SDS) surfactant was more suitable for the preparation of TFN membrane. The reaction time determined the extent of interfacial polymerization and the integrality of surface skin layer. Furthermore, the nanofiltration properties of the MWNTs/polyester TFN membrane were tested by examining the separation performance of different feed solutions, feed concentrations, feed pHs at 0.6 MPa operating pressure. Additionally, the MWNTs/polyester TFN membrane exhibited a good long-term stability.
<<全文链接>>

