Near-Frictionless Long-Distance Water Transport in Trees Enabled by Hierarchically Helical Molecular Pumps
Citation
Yanjun Liu, Jialin Zhang, and Peiyi Wu*. Near-Frictionless Long-Distance Water Transport in Trees Enabled by Hierarchically Helical Molecular Pumps. CCS Chem. 2025, 7, 484-492.
Abatract
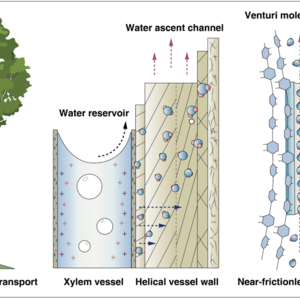
The ascent of water in tall trees has fascinated scientists for over 130 years. However, the microscopic state and dynamic behavior of water within natural and undisturbed trees remain unknown. Here, we employed low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to monitor in situ the distribution and movement of water within a living tree, uncovering a counterintuitive water transport process. The hierarchical walls of xylem vessels served as the primary channels for continuous ascent of water, while the xylem vessels functioned more like a temporary water reservoir. The helical nanofibers within the vessel walls, which consisted of series-wound crystalline and amorphous regions, created a helical Venturi molecular pump structure that could efficiently draw water from the xylem vessel reservoir. Importantly, these helical nanofibers possessed a semi-disordered surface embedded with a layer of solid-state water akin to a layer of ice. This self-lubricating layer of ice-like monolayer water, combined with the new “ground level” created by the helical arrangement of nanofibers, enabled virtually frictionless long-distance transport of water under low negative pressure. Our findings challenge existing theories and offer valuable insights for developing biomimetic fiber pumps, characterized by high efficiency and low energy consumption in fluid transportation.